Agreement is a project document and is the input for Develop Project Charter, Determine Budget processes and the output of Conduct Procurements process.
I know many of you must be aspiring to become successful project managers in your career which can be the stepping stone to become good leaders. How you can achieve this? Yes, by implementation which is critical. And to distinguish from others you need to have some kind of credentials which can be obtained through certifications like PMP, ITIL. To know more about or to get prepared for the same, you can always approach me @ bksprasad@yahoo.com or subramanya.bks@gmail.com
Wednesday, April 20, 2016
Agreements
Business Case
Business case is created because of legal requirement, technology change, organization change, market demand, to serve the social need, customer request, ecological impacts. The project manager should follow the life cycle efficiently and effectively to meet the business need.
Business Case is the input for Develop Project Charter process.
Tuesday, April 19, 2016
Project Statement of Work
Business need provides the need of the project which can be because of legal, technology, market conditions, new initiative, etc…
Product scope description is about the characteristics of the product, service or result which we are going to achieve. It should be in relationship with business need.
Strategic plan is about the goal, vision and objective in alignment with organizational strategy and vision.
Project Statement of Work is a project document and is in the input for Develop Project Charter process.
Monday, April 18, 2016
Stakeholder Analysis
•Identify the potential stakeholders, their contact information, from which function they belongs to, external or internal, their needs, roles, etc.. It is difficult to identify all the stakeholders in the beginning. To overcome this challenge identify the key stakeholders such as sponsor, primary customer and involve them and use the other techniques like Meeting, Expert Judgment to identify the potential stakeholders. Of course identification of stakeholders has to happen throughout the project.
•Understand each stakeholder impact and support, so that accordingly you can prioritize the communication in an efficient manner.
•Assess how the stakeholders may react to different situations which help in identifying the threats for the project.
There are different models which can be developed with Stakeholder Analysis: Power vs Interest grid, Power/Influence grid, Influence vs Impact grid and Salience model which considers three parameters namely power, urgency and legitimacy.
The diagrams below show the Power vs Influence grid and the Salience Model.


Stakeholder Analysis technique is used under the process Identify Stakeholders.
Sunday, April 17, 2016
Procurement Audits
Procurement Audits technique is used under the process Close Procurements.
Friday, April 15, 2016
Records Management System
Records Management System tool is used under the processes Control Procurements and Close Procurements.
Thursday, April 14, 2016
Claims Administration
Claims Administration technique is used under the process Control Procurements.
Wednesday, April 13, 2016
Payment Systems
Payment Systems technique is used under the process Control Procurements.
Tuesday, April 12, 2016
Inspections and Audits
Inspections and Audits technique is used under the process Control Procurements.
Monday, April 11, 2016
Procurement Performance Review
Procurement Performance Review technique is used under the process Control Procurements.
Thursday, March 31, 2016
Contract Change Control System
Contract Change Control System technique is used under the process Control Procurements.
Wednesday, March 30, 2016
Procurement Negotiations
The project manager should involve other project management team while negotiation with seller so that it will assist in understanding the technical, quality and management requirements.
Also Procurement Negotiations are used if any disputes, outstanding issues, claims during the closing of procurements. If this is not working, one can use Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) through mediation. In the worst case it has to be settled in the court which is least preferred.
At the end of the day the Procurement Negotiations should be from win-win proposition.
Procurement Negotiations technique is used under the processes Conduct Procurements and Close Procurements.
Tuesday, March 29, 2016
Advertising
Advertising technique is used the process Conduct Procurements.
Independent Estimates
For example if the bidding price is $20K and our estimation is $15k, this is a considerable gap. The reasons can be either the scope understanding from the seller side is incorrect or the buyer has not done his estimate properly.
Independent Estimates techniques is used the process Conduct Procurements.
Wednesday, March 23, 2016
Proposal Evaluation Techniques
Proposal Evaluation Techniques is used the process Conduct Procurements.
Tuesday, March 22, 2016
Bidder Conferences
Bidder Conferences technique is used the process Conduct Procurements.
Monday, March 21, 2016
Market Research
Market Research technique is used under the process Plan Procurement Management.
Sunday, March 20, 2016
Make-or-Buy Analysis
Sometimes the budget constraints also influence make-or-buy decisions. In either case we need to consider both direct and indirect costs. Also once we decide on buy decision the type of contracts need to be considered based on the risk sharing between the buyer and seller.
The Make-or-Buy Analysis results in Make-or-Bye Decisions.
Make-or-Buy Analysis technique is used under the process Plan Procurement Management.
Thursday, March 17, 2016
Technical Performance Measurement
Technical Performance Measurement technique is used under the process Control Risks
Wednesday, March 16, 2016
Risk Audit
Tuesday, March 15, 2016
Variance and Trend Analysis
Variance and Trend Analysis technique is used under the process Control Risks.
Monday, March 14, 2016
Risk Reassessment
Risk Reassessment technique is used under the process Control Risks.
Friday, March 11, 2016
Contingent Response Strategies
Contingent Response Strategies technique is used under the process Plan Risk Responses.
Thursday, March 10, 2016
Strategies for Negative Risks or Threats and Strategies for Positive Risks or Opportunities
Avoid is used when you don’t want to get into the situation. Example: avoiding the scope, extending the schedule, changing the strategies and even avoiding the project itself. This response is used when the risk ranking is high with high probability and high impact.
Transfer is shifting the risk to some other party. By transferring the risk means not disowning the risk. Still the project team owns the risk but usually transfer from the financial angle. For example Insurance, bonds, warranty, guarantee or even transferring some of the work/scope back to the customer. This response is used when the risk is at lower ranking.
Mitigation is reducing the probability and/or impact to the situation. For example providing the training to the staff when there is no expertise available, having the standby machines when the primary fails. This response is used when the risk ranking is high with high probability and high impact.
Accept is acknowledge the risk and don’t take any action till it materializes. There are two types of acceptance. One is passive and second is active acceptance. Passive acceptance is don’t do anything. When it happens then get into action. For example you know that machine is going to be down. When goes down then only you will try to get another one or repair it. Active acceptance is preparing for contingency reserve in terms of cost, schedule or resource. This response is used when the risk is at lower ranking.
Exploit is used to realizing the opportunities. For example early delivery to get more business, use latest technology to save cost. Here the team ensures that risk materializes and the response is in an aggressive manner.
Share is allocation of entire or partial risk to some other third parties to gain benefits. For example joint venture, partnership.
Enhance is increasing the possibility of occurrence of risk by increasing the probability and or impact. This is similar to Exploit but not in an aggressive way. For example, adding the resources to complete the project early.
Accept is taking the opportunity if it occurs, but not activity pursing it.
Strategies for Negative Risks or Threats and Strategies for Positive Risks or Opportunities techniques used under the process Plan Risk Responses.
Wednesday, March 9, 2016
Quantitative Risk Analysis and Modeling Techniques
Sensitivity analysis is used when we change any of the variables what can be the impact on the end result. The most common diagram used under Sensitivity analysis is Tornado diagram. It is a bar chart to compare the relative importance of the variables. The y- axis consists of different risks and the x axis represents uncertainties for range for each of these risks in the form of bar chart and is drawn from highest length to the lowest length of the bars.
Expected monetary value analysis helps in finding which is riskier by comparing two different scenarios. For example is it worth to buy equipment or build on your own. The calculation is based on initial investment, probability and impact. The higher the value better is the option.
Modeling and simulation technique uses Monte Carlo simulation analysis by choosing the random values for each iteration and provides what should be the contingencies for every risk.
Quantitative Risk Analysis and Modeling Techniques is used under the process Perform Quantitative Risk Analysis.
Sunday, March 6, 2016
Data Gathering and Representation Techniques
An interview is to gather information from experts based on historical information. While collecting the probability and impact there may be situation stakeholders having difference of opinion. For example for a particular risk one may say the probability is 20%, the other stakeholder may say the probability is 40% and one more stakeholder may say it is 80%. So we can use three point estimation (PERT) to arrive the more approximate or realistic value. Similarly it is applicable for Impact.
Probability distribution uses two types one is Beta distribution and the second is Triangular distribution. These distributions provide the relative likely hood of risks in terms of cost and time.
Data Gathering and Representation Techniques is used under the process Perform Quantitative Risk Analysis.
Saturday, March 5, 2016
Risk Urgency Assessment
Risk Urgency Assessment technique is used the process Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis.
Friday, March 4, 2016
Risk Categorization
Risk Categorization technique is used under the process Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis.
Thursday, March 3, 2016
Risk Data Quality Assessment
Risk Data Quality Assessment technique is used under the process Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis.
Wednesday, March 2, 2016
Probability and Impact Matrix
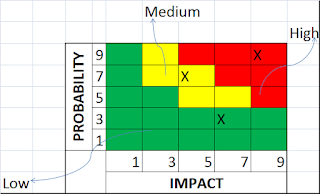
Probability and Impact Matrix technique is used under the process Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis.
Tuesday, March 1, 2016
Risk Probability and Impact Assessment
Once you identify the risks we can’t address all the risks with same priority. One needs to assess the probability and Impact by using the scaling. For example probability with >80% can be of higher scale and <10% can be in the lower scale. Similarly for the impact we can use the scaling factor. If the impact is >$40K then scaling is high <$5K the scaling low. The definitions of these scales are defined as part of Risk Management plan. By using this one can arrive the risk priorities like high, medium, low…
If the risk ranking is low it should be kept as watch list.
Risk Probability and Impact Assessment technique is used under the process Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis.
Monday, February 29, 2016
SWOT Analysis
For example the strength can be availability of the funding. Make this as an opportunity for investing on team by providing training or competency development which helps in making the project success. Process is not in place is a weakness and this can be a threat for the final outcome of the quality product. Take different risk responses like mitigate/transfer to come out of the situation.
SWOT Analysis technique is used under Identify Risks Process.
Thursday, February 25, 2016
Assumptions Analysis
Assumptions Analysis technique is used under the process Identify Risks.
Wednesday, February 24, 2016
Checklist Analysis
Checklist Analysis is used under the process Identify Risks process.
Tuesday, February 23, 2016
Information Gathering Techniques
Brainstorming is useful in collecting detailed information and useful in identifying risks. This can be carried out by involving experts by having a moderator and can be in an informal way or structured way. Brainstorming helps in out of box thinking and idea generation which helps in identifying risks.
Delphi technique is used to collect all the information in an anonymous or secret manner. A facilitator collects all the data from stakeholders in a different forum and shares the information with all the stakeholders without mentioning the names of the stakeholders just to avoid conflict of interest.
Interviewing is having discussions with project stakeholders, experts to gather the information.
Root Cause Analysis is finding out underlying causes of an issue and preventing future damages.
Information Gathering Technique is used under the process Identify Risks Process.
Documentation Reviews
Documentation Reviews technique is used under the process Identify Risks.
Friday, February 12, 2016
Performance Reporting
The format, frequency has to be understood from the stakeholders during the planning and accordingly need to be distributed. The reports may include, past performance, forecasting, status of risks and issues, work completed, work to be completed in the immediate future, change request status and any other relevant information.
Performance Reporting technique is used under the processes Manage Communications and Control Procurements.
Thursday, February 11, 2016
Information Management Systems
Hard copy documents like memos, letters, press releases, notes
Electronic Communication Management like video conference, fax machines, email exchange servers, audio conferencing, telephone, web pages
Electronic project management tools like scheduling tool, project management software tool, MS Project
It is part of PMIS.
Information Management Systems tool is used under the processes Manage Communications, Control Communications and Control Stakeholder Engagement
Wednesday, February 10, 2016
Communication Methods
Interactive communication: This is two ways and the stakeholders exchange information between them by face to face, video conferencing, instant messaging, audio conferencing.
Push communication: The sender broadcasts the message to the intended stakeholders. Even the message is distributed, there is no guarantee that the receiver received and or understood. Examples are email, memos, fax, blogs, voice mail.
Pull communication: The receivers retrieves the messages based on their convenience. Typically used for large files or for large audience. Examples are shared folders, e-learning, repositories.
Communication Methods needs to be understood from all the stakeholders and accordingly it is used.
Communication Methods technique is used under the processes Plan Communications Management, Manage Communications and Manage Stakeholder Engagement.
Tuesday, February 9, 2016
Communication Models
Sender: The one who send the message.
Encoder: The information is translated by the sender.
Transmit message: The information is sent through medium.
Medium: The mode/channel through which the message is conveyed. It can be email, fax, telephone, video conferencing, etc…
Decode: The receiver translate the message from sender to his/her understandable language.
Noise: Noise is compromised message and is inevitable. The examples can be unfamiliar technology, distance, culture difference, the technology itself and lack of background knowledge.
Acknowledge: The receiver confirms he/she received the message. But that doesn’t mean he/she is agreeing for the message.
Feedback/Response: The receiver again encodes the message and sends to the original sender about his/her thoughts. The receiver (original sender) decodes the message back to his/her understandable language.
Communication Models technique is used the processes Plan communications Management and Manage Communications.
Monday, February 8, 2016
Communication technology
Urgency is how quickly the information to be shared and what the frequency is. This varies from project to project.
Technology availability is based on organization accessibility, compatibility and financial capability.
Ease of use is how feasible to use the technology and the stakeholders need to be educated about the use of technology.
Project environment includes culture, time zone, language, the preference like face-face or virtual.
Sensitivity and confidentiality of the information exchanged where security factor to be considered.
Communication Technology technique is used under the process Plan Communications Management.
Saturday, January 30, 2016
Communication Requirements Analysis
Also we need to identify the possible number of communication channels within the project. It is calculated using the formula n(n-1)/2 where n is number of stakeholders. For example if there are 10 people, then the number of communication channels will be 45. This helps in how much of time the project manager has to devote for the communication aspects.
The sources of analysis can be from stakeholder register, organization charts, responsibility relationships, department, external information needs like government, vendors, internal communication needs like between the functions, location, etc…
Communication Requirements Analysis technique is used under the process Plan Communications Management.
Thursday, January 28, 2016
Project Performance Appraisals
Project Performance Appraisals depends on organization policy, complexity of the project, budget, frequency, length of the project, labor laws as per the contract.
Project Performance Appraisals technique is used under the process Manage Project Team.
Wednesday, January 27, 2016
Observation and Conversation
Observation and Conversation technique is used under the process Manage Project Team
Tuesday, January 26, 2016
Personnel Assessment Tools
Monday, January 25, 2016
Recognition and Rewards
Recognition and Rewards technique is used under the process Develop Project Team.
Sunday, January 24, 2016
Colocation
Colocation technique is used under the process Develop Project team.
Saturday, January 23, 2016
Ground Rules
For example the team should come on time to the meetings and the meetings should end on time. While inviting for the meeting the clear agenda has to be set.
Ground Rules is used under the process Develop Project team.
Friday, January 22, 2016
Team Building Activities
The project environment is very much dynamic because of the movement of the people, organizational changes, and individual attitude towards the work. The project manager needs to monitor these project environmental changes and use the team building activities technique throughout the project.
The model which can be used is Tuckman ladder. There are five stages under this model namely Forming, Storming, Norming, Performing and Adjourning.
Forming is the team formation and assigning the roles and responsibilities.
Storming is the stage where the people having difference of opinions, clashes, conflict.
Norming is the team start adjusting toward the environment and begin to work.
Performing is the team is interdependent and starts achieving the results.
Adjourning is disbanding to their respective functions.
Team Building Activities technique is used under the process Develop Project team.
Thursday, January 21, 2016
Training
Training technique is used under the process Develop Project Team.
Wednesday, January 20, 2016
Conflict Management
Collaborating or Problem Solving: The team is open to discuss the difference of opinion and come with different solutions and take the decision with consensus. This results in win-win situation. For example removing the overlapping of the activities, finding the different alternate solutions for the issue and getting the consensus from all the people and implementing the solution, applying one of the solutions and if not working going for the other solution.
Compromising or Reconciling: It brings some degree of satisfaction to both the parties and is lose-lose situation since no party gets fully satisfied. This is the next best after collaborating. For example taking 50% solution one party and 50% solution from another party and implementing it, considering the cost over the schedule.
Withdrawal or Avoidance: Here the parties defer the decision of a problem to a later time or date. This is not the best technique but can be applied based on the situation. For example let’s deal this next week, come to my office and will discuss later, let’s take it offline.
Smoothing or Accommodating: Here areas of agreement are focused rather than areas of disagreement. To maintain the relationship and harmony this technique is used. For example calming down the situation to get into work where there is chaos over issues.
Force or Direct: Pushing one viewpoint at the expense of another and results in win-lose situation. Again this technique can be used if no other techniques are working out and can be last resort. For example using the power and directing the team to work.
Collaborating is the best Conflict Management technique.
Conflict Management is used under the process Manage Project Team.
Interpersonal Skills
Leadership: It is the ability to get the things done. It involves focusing the efforts of a group of people toward a common goal and enabling them to work as a team. To achieve the goal one need to set the vision and maintaining it. Apart from trust building we need to respect, influencing, monitoring, and mentoring the team.
Team building: Team building is helping the individual and the group to grow and make the project success. We need to set the good environment so that the team starts trusting with each other and work towards the project. To achieve this the project manager should set right process, enhancing the team skills by facilitating the training programs, on site and off site meetings, etc..
Motivation: Most of the time the level of work which the people can contribute to the project depends on their motivational level. The project manager should motivate the team by assigning the challenging work or the work which they value most, appreciation, appropriate compensation, rewards and recognition.
Communication: Communication is the key factor for success or failure of the project. It should be always two ways. The project manager spends 90% of the time to ensure proper communication is happening from him and among the stakeholders. Conveying the right information, at the right time, to the right stakeholders using right media is called communication. It should be efficient and effective. The project manager should be a good listener. He should understand or recognize tone, modulation, body language.
Influencing: Influencing is to get others co-operate in making the project success. It can be achieved by setting himself/herself as an example, having and concluding the decisions in a collaborative way, adjusting the style as per the situation or environment, applying the power cautiously.
Decision Making: Four decision styles are command, consultation, consensus and coin-flip and four factors which affect decision styles are time constraints, trust, quality and acceptance. Decision making model can be described by six-phase model namely
Problem Definition
Problem Solution Generation
Ideas to Action, Solution Action Planning,
Solution Evaluation Planning
Evaluation of the Outcome and process
Political and cultural awareness: The project manager should understand and use the power and politics within the project environment. Organizational politics are inevitable. Avoiding these two factors may lead to unsuccessful projects. The team will be working with global environment and the factors like language, culture can influence in a negative manner and can hinder the progress of the project. So, we need to create the trust environment and win-win atmosphere.
Negotiation: Refer to the link http://bksprasad.blogspot.in/2016/01/negotiation.html
Trust Building: Without trust building across the project team and the stakeholders we can’t make the project success. Trust building can be done through
Open and honest communication
Informing the stakeholders about the right project status and the risks associated
Spending time with team to eliminate assumptions
Voicing your need directly
Not withholding the information out of fear
Open to innovation
Working towards project interest
Having concern about other opinions
Conflict Management: Refer to the link http://bksprasad.blogspot.in/2016/01/conflict-management.html
Coaching: Coaching technique is to develop the skills of the people to maximize their potential. It can be formal or informal. It results in motivation, confidence building, develop confidence and positivity. Counseling is different from coaching. Counseling addresses won’t whereas coaching addresses can’t and will convert to can. By using this technique the chances of making the project success is more.
Interpersonal Skills has to be applied throughout the project and is a technique used under the processes Develop Project Team, Manage Project Team and Manage Stakeholders Engagement.
Tuesday, January 19, 2016
Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis
Availability: The project the team or the person should be available during the required schedule.
Experience: Relevant experience of the team which matches the project requirement.
Cost: The cost which will be incurred for the team is it within the budget?
Ability: Apart from experience, the person ability to see is he/she competent enough to carry the work?
Attitude: The style of the member/s whether they cope up with the environment or not.
Knowledge: Relevant knowledge of the customer, project implementation
Skills: Relevant skills to use the tool
International factors: Time zone, language, communication skills, location
Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis technique is used under the process Acquire Project Team.
Monday, January 18, 2016
Virtual Teams
For the team from the same organization but spread across different geographical locations.
For the expertise from external who are in different geographical areas
For the people who work from home
For the people who work in different shifts, hours or days
For the people who are physically challenged due to disability
For the organization where the organization can minimize the travel cost
Virtual Teams can lead to some disadvantages like misunderstanding, sharing knowledge, isolation. For any critical discussions or issues to be solved face to face is the best option. However one can choose the Virtual Teams options cautiously to create the team.
Virtual Teams technique is used under the process Acquire Project Team.
Sunday, January 17, 2016
Acquisition
Acquisition technique is used under the process Acquire Project Team.
Thursday, January 14, 2016
Negotiation
Functional manager to get the best resources for your project with specific skills for specific time.
Other functions within the organization when there is a scarce resource.
Vendors, suppliers to get the qualified and certified resources.
Negotiation happens with every stakeholder in one way or the other throughout the project. But Negotiation should end from win-win perspective.
Negotiation technique is used under the processes Acquire Project Team.
Wednesday, January 13, 2016
Pre-assignment
Pre-assignment technique is used under the process Acquire Project Team
Tuesday, January 12, 2016
Organizational Theory
Organizational Theory technique is used under the process Plan Human Resource Management.
Monday, January 11, 2016
Networking
Networking technique is used under the process Plan Human Resource Management.
Sunday, January 10, 2016
Organization Charts and Position Descriptions
Hierarchical-type charts are used to show te positions and the relationships between department and or people. It’s like organizational breakdown structure (OBS). It shows departments, units or team with project activities or work packages that will be executed under each department.
Matrix-based charts are used to show the responsibility assignment matrix (RAM) and uses RACI charts or the model. R is responsibility, A is Accountable, C is Consult and I is Inform. Responsible means the people who are working on the activity, Accountable is the person who is having ownership for an activity, Consult is the people to who we need to have discussion so that approval can be obtained like SME, consultant and Inform is the people to who we have to just keep in loop for the message exchanges. For any activity only one should be accountable and we can have multiple responsible, consult and inform.
Text-oriented formats are detailed descriptions of the roles and responsibilities, authority, competencies and qualifications of the individual or the team can be mentioned.
Organization Charts and Position Descriptions technique is used under the process Plan Human Resource Management.
Saturday, January 9, 2016
Approved Change Request Review
Approved Change Request Review technique will ensure the approved changes are implemented correctly.
Approved Change Request Review is used under the process Perform Quality Assurance.
Friday, January 8, 2016
Process Analysis
Process Analysis technique is used the process Perform Quality Assurance
Thursday, January 7, 2016
Quality Audits
Some of the outcome of the Quality Audits will be:
Identification of non- conformance which means the project is not following the desired steps
Identification of best practices from your projects which can be implemented for other projects
Identification of best practices from other projects which can be considered for your projects
Proactive measures which can be taken to improve the processes which in turn help in team raise productivity
Contribution of each audit in the lesson learned organizational knowledge bank
Quality Audits can be random or scheduled basis. Also this technique ensures implementation of approved change requests.
Quality Audit is used under the process Perform Quality Assurance which is part of Executing process group.
Wednesday, January 6, 2016
Quality management and control tools
For Affinity diagram refer the link http://bksprasad.blogspot.in/2015/09/group-creativity-technique.html
Process decision program charts (PDPC): is used to understand the goal in relation to the steps to be followed in achieving the goal. This helps in anticipating the risk which may arise while achieving the goal so as to plan for contingency.
For example automation is to be introduced. Choice is buy a tool or build it yourself. Buy the tool decision leads to vendor selection and ordering. If the vendor will not deliver it on time what can be contingency plan. Similarly build it yourself decision leads to hiring resources. If the desired skilled resource not available what can be the contingency? It may be train the existing employees. This entire sequence can be represented as diagram.
Interrelationship diagraphs is used in problem solving by connecting the relationship with one cause to other the other cause. This can be developed using other diagrams like affinity diagram, cause and effect diagram.
For example the customer is using lot of defects. What can be the reason? The reason can be lack of understanding of the requirements, poor design, improper development, incomplete testing. Let us the major defects are due to incomplete testing which has been found out by cause and effect diagram. The cause of incomplete testing can be poor test planning, the cause for poor test planning can be the requirements came late, this cause can be the customer did not provide the requirements as per the committed date. In this way we can relate the causes and draw the diagram.
Tree diagram used to represent decomposition hierarchies like Work Breakdown Structure, Risk Breakdown Structure and Organizational Breakdown Structure. After creating this structure it terminates to the single point which helps in taking the decision.
For example in a coin what is the probability of getting head or tail? It is 50%. So the value for each possibility is 0.5. Let’s add one more coin and tossing both the coins, the combinations increases to HH, HT, TH and TT. So the probability of getting atleast one head in this scenario will be 75%. Using this mechanism one can design the process improvement or reducing the product defects.
Prioritization matrix: Here the issues are identified and the alternatives are found and prioritized to solve the issue by giving the weightages. For example, need to complete a deliverable which requires highly skilled people and are not available within the organization. The alternatives are outsource or train the existing employees. Give the weightages for both the options and see what can be the best outcome. The one which scores higher is the better option.
Activity network diagrams are nothing but project network diagram. It is used with scheduling, PERT, CPM and PDM. To understand these diagrams refer to the links:
http://bksprasad.blogspot.in/2015/11/three-point-estimating.html
http://bksprasad.blogspot.in/2015/11/critical-path.html
http://bksprasad.blogspot.in/2015/10/precedence-diagramming-method-pdm.html
Matrix diagrams used to perform data analysis created in matrix form. The matrix diagram can be created using rows and columns with different parameters and will indicate the strength of the relationships between those parameters.
Perform quality Assurance process uses Quality Management and Control Tools in addition to the tools which are used under processes Plan Quality management and Control Quality.
Additional Quality Planning Tools
For Brainstorming and Nominal group techniques you can refer to the link http://bksprasad.blogspot.in/2015/09/group-creativity-technique.html
Force field analysis provides the diagram to the situations which is for and against. For example we need to introduce automation system instead of manual. The for can be increased efficiency, consistency in getting the results, easier monitoring, cutting the human resource cost whereas the against can threat to the job, initial investment, demotivation among the staff which can results in attrition at the organization level, disruption of service till gets stabilized. For each of these parameters we can give the weightages and sum it. The total score can be used to decide based on the highest score to consider automation or not.
Quality management and control tools are Affinity diagram, Process decision program charts, Interrelationship digraphs, Tree diagrams, prioritization matrices, Activity network diagrams and Matrix diagrams. These seven tools are called Seven Quality and Control Tools.
For Affinity diagram refer the link http://bksprasad.blogspot.in/2015/09/group-creativity-technique.html
For the remaining tools refer the link http://bksprasad.blogspot.in/2016/01/quality-management-and-control-tools.html
Additional Quality Planning Tools is used under the process Plan Quality Management.
Tuesday, January 5, 2016
Statistical Sampling
Statistical Sampling technique is used under the process Plan Quality Management and Control Quality.
Monday, January 4, 2016
Design of Experiments
Design of Experiments is used under the process Plan Quality Management.
Sunday, January 3, 2016
Seven Basic Quality tools
Cause and effect diagrams: This tool is used to find the cause for a particular defect/effect. The defect or the problem statement is defined and causes for this defect is identified. Then one can use the concept “5 Why’s” to find out the root causes which can be converted to actionable items. When you represent the problem statement and the causes in the form of visual representation, it looks like a fish skeletal hence the name fish bone diagram and is also called as Ishikawa diagram.
Flowcharts: Flow charts depict the flow of the work or the process which is sequence of steps to be carried out. Flowcharts show the activities, decision points, branching loops, parallel paths, inputs, outputs… It uses a model called SIPOC, Supplier-Input-Process-Output-Customer, or the COPIS, Customer-Output-Process-Input-Supplier, model. For example, in the car manufacturing industry, the supplier provides the raw materials as the input, the process manufactures the car which is the output and is used by the customer. The customer provides the feedback which helps in improving the process and in turn the raw materials quality from the suppliers. The workflow logic and the frequency helps in expected monetary value for conformance and nonconformance work to deliver the desired output which in turn helps in estimating the cost of quality.
Checksheets: This is also called as tallysheet used to gather data. Checksheets ensures that all the data has been gathered which helps in identifying potential problems. This helps in inspection to identify the defects. For example there is a product which about 10 cm length which is the expected value. The other possible values which we can get are >10cm or <10cm. Measure all the output and see how many are meeting the expected value and how many or not.
Pareto diagrams: This is also called as 80/20 rule used to find most potential issues or to distinguish between critical vs non-critical. 80/20 rule means 80% of the problems are due to 20% of the causes.
Histograms: It is a bar chart and used to find the central tendency, dispersion and shape of statistical distribution. Also histogram can be used to represent data in no particular order and is not related to time. The bar which is higher can be the reason for the defect or effect.
Control charts: This tool is used to see if the process is stable or not and also to find the measurements are coming within the expected limits. Control charts uses four parameters apart from mean, upper specification limit (USL), lower specification limit (LSL), upper control limit (UCL) and lower control limits (LCL). The mid line will be mean, the line immediately above mean is UCL and the still above that is USL and the line immediately below mean is LCL and the one which still below is LSL. If the measurements are within the UCL and LCL then there is no problem. If the measurements are above the UCL and or below the LCL then it calls for corrective action. There is one more principle called rule of seven. Rule of seven says if the 7 consecutive points are above the mean level or seven consecutive points are below mean level and even though they are within the control limits still it calls for corrective action. USL and LSL can be customer committed values above which the measurements are not acceptable. UCL and LCL are defined within the project level in agreement with stakeholders. UCL and LCL helps in tightening the situation so that we are not touching or deviating the specification limits.
Scatter diagrams: This is also called as correlation charts used to find is there any relation between two variables. The correlation can be positive or negative or zero. Based on positive and or negative it helps in taking further action.
The above 7QC tools can be used as combination.
Seven Basic Quality Tools is used under the process Plan Quality Management, Control Quality. This is also used along with seven quality management and control tools, which is used under the Perform Quality Assurance process.